When Oil and Gas Companies Go to School
Funding for university research programs by the oil and gas (O&G) industry is increasingly controversial in the United States. A 2023 Guardian article, for instance, described student “unease” upon learning that an Exxon employee maintained an office and teaching responsibilities at Princeton University. A 2024 bicameral congressional report, Denial, Disinformation, and Doublespeak: Big Oil’s Evolving Efforts to Avoid Accountability for Climate Change, found that more than 80 US universities receive funding from O&G corporations, which sometimes includes the payment of hundreds of millions of dollars and can go on for decades.
In light of such investigations, many students and administrators have concluded that all engagement with O&G companies should be off limits to academic researchers. Some academic institutions have not only stopped accepting research funding; they have also divested from any financial engagement with O&G companies, including withdrawing their endowment investments. While I am firmly in agreement that we need to take decisive, rapid action to address climate change, I argue that there is no good one-size-fits-all answer to the question of whether accepting O&G funding is ethical or compatible with a university’s objectives. Instead, I propose a framework that schools can use to evaluate potential research funding relationships with O&G companies in light of their own values.
I argue that there is no good one-size-fits-all answer to the question of whether accepting O&G funding is ethical or compatible with a university’s objectives. Instead, I propose a framework that schools can use to evaluate potential research funding relationships with O&G companies in light of their own values.
Researchers, administrators, and the broader academic community are best served by a practical approach to the question of engaging with corporations in the O&G business—one that appreciates the ubiquitous role of fossil fuels in the modern world in providing low-cost energy and transportation, the urgency in addressing climate change, and the variety of ways that labs and O&G companies can engage, as well as the many types of research that are possible. It’s also important to recognize the many important societal values that intersect around the O&G industry—including equity, climate change mitigation, energy availability and cost, societal resilience, and energy security.
Accepting research funding from O&G companies involves making complex trade-offs among those societal values. For example, research dedicated to helping O&G companies increase the supply of fossil fuel resources is the most controversial kind of engagement, but many people would argue that fossil fuels are an inexpensive and ubiquitous source of energy—particularly in regions where fossil fuel is extracted—and is a necessary part of an overall energy solution. Moreover, the expertise associated with fossil fuel extraction is increasingly being deployed for decarbonization efforts, such as carbon storage or geothermal energy.
Similarly, O&G companies are also investing in university research and development in areas like green hydrogen or sustainable aviation fuel production, again leveraging the deep expertise of the O&G industry in fuels processing, but toward a greener energy transition. For some observers, these societal costs and benefits warrant carefully designed partnerships, but others argue that any engagement with the O&G industry is inherently unethical because of the role these companies have played in climate change.
Naturally, different researchers engage with these different points of energy availability, resilience, and security in different ways. Moreover, while science can answer questions about the climate effects of putting more carbon into the atmosphere, it cannot quantify how to weight the important societal values of climate change mitigation, job stability, or energy security. Distinct academic communities, emphasizing different values, will understandably reach different conclusions about what kinds of relationships between the university and O&G industry are worthwhile or justified. The important thing is that these communities carefully examine the ramifications of those conclusions and proceed intentionally and thoughtfully.
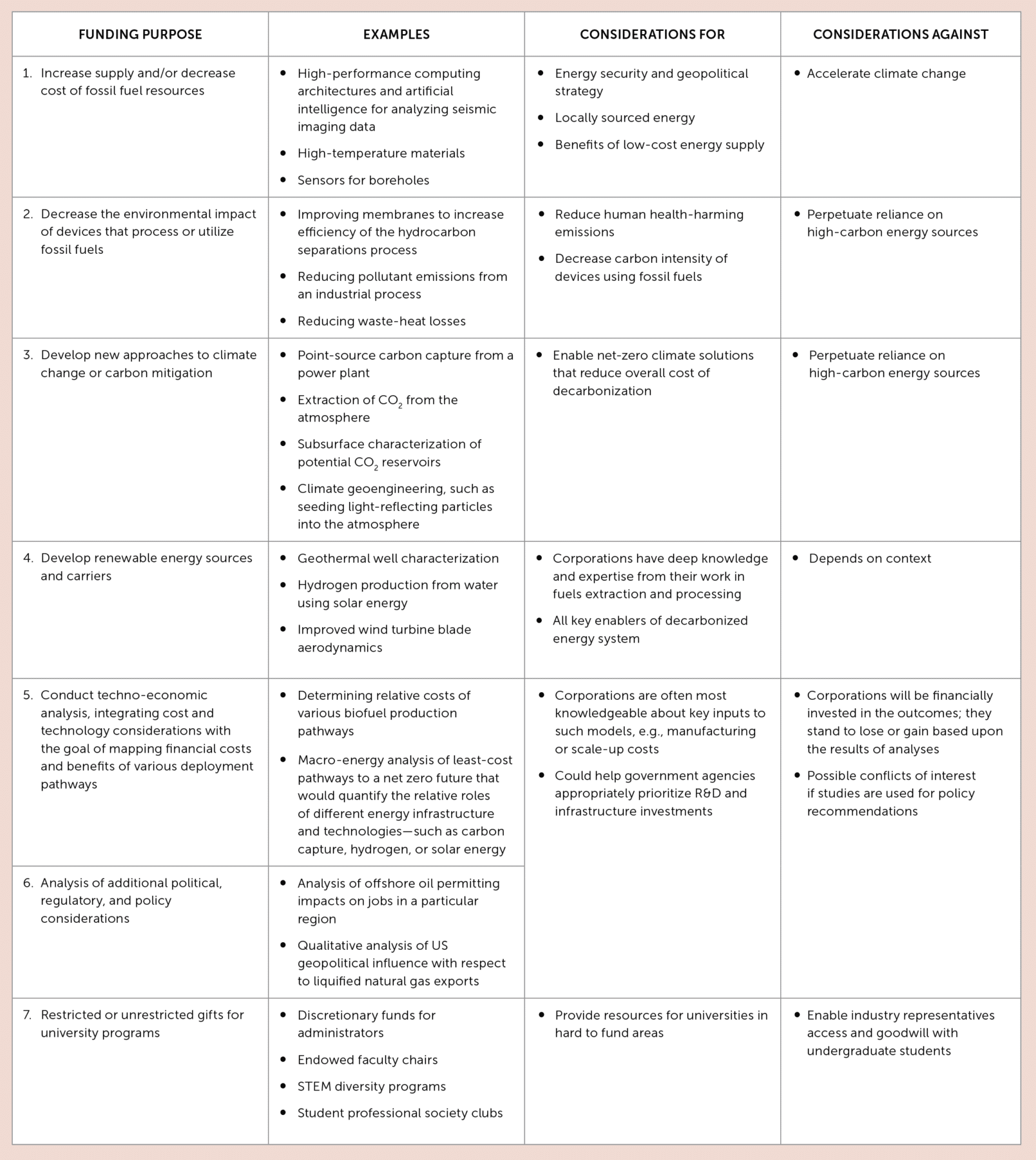
Inherent in these considerations is that the various forms of engagement with the O&G industry can be radically different, and it is not helpful to paint all O&G engagements with the same brush. To help researchers, students, and administrators explore these funding relationships systematically, I have composed the table at left depicting a range of engagement points based on the funding purpose.
Although the trade-offs among items 1–4 are relatively straightforward, items 5 and 6 introduce additional conflict-of-interest considerations, particularly in the area of making policy recommendations, which could include government regulations or use of government funds. Managing such possible conflicts of interest is very difficult and may be impossible in some cases. And then there are more general issues of companies’ building goodwill with a community, which are covered in item 7. Here, a company may support a student, faculty member, or leadership position in a university, in much the same way as companies provide grants to a broad set of societal organizations (such as Little League Baseball) that have little relationship with their core business. A university may not want to approve such corporate relationships with its community.
By clarifying the different kinds of relationships and purposes of the research, academic communities can look more carefully and specifically at individual projects and their potential contributions. They can also discuss the dangers such projects raise for conflicts of interest. For example, funding for research aimed at making the extraction of oil cheaper or faster will be controversial in many university departments, while funding for research devoted to the development of sustainable carbon-free alternative energy technologies will be less so.
Determining the purpose of an engagement—from both the university’s point of view and industry’s—will not necessarily settle the question of whether to embrace a project or not, but it can serve as the foundation from which to launch a constructive debate.
Determining the purpose of an engagement—from both the university’s point of view and industry’s—will not necessarily settle the question of whether to embrace a project or not, but it can serve as the foundation from which to launch a constructive debate. There may even be cases where industry collaboration is essential for research progress because O&G companies hold the only data and expertise needed to even conduct the research. There may be others where the conflict of interest—or perceived conflict—is so great it would disqualify almost any research.
The stakes could hardly be higher. It is imperative that society moves quickly to reduce its climate impacts, but also to support marginalized communities and avoid economic or social disruption. The university research community plays a central role in that process, but it must adhere to high standards. Fostering nuanced thinking and transparent disclosure processes can help balance the pursuit of knowledge and innovation with the imperative to promote sustainability, equity, and economic opportunities for all.
